

In order to configure NFSv4, you’ll need Kerberos to manage the KDC, which in turn will refer to a listing of users and their permissions. When monitoring the system’s performance, be on the lookout for disk contention. The speed of the storage disks and the amount of NFS writes factor into whether or not the NAS system would benefit from the addition of a mirrored SLOG. By default, NFS writes are always sync, though some NFS clients can override that default when mounting the NFS share (even though mount(8) warns that doing so is a bad idea). Our article on Understanding OpenZFS SLOGs provides a good overview on the differences between async and sync writes, and how that the difference impacts an OpenZFS system. For example, it requires that a configured KDC (Key Distribution Center) and directory service are available in the network to provide user authentication. Not surprisingly, NFSv4’s slew of new features increases its configuration complexity. Refer to pnfsserver(4) and pnfs(4) for configuration information. FreeBSD supports pNFS (parallel NFS) for high-performance storage using NFSv4.2.NFSv4 implements the RPSEC_GSS protocol standard to provide authentication, integrity, and privacy over the network between the NFS server and client. NFSv3 security is limited to file permissions on the exported data and allowed host addresses defined in the exports file.In NFSv4, exports can be mounted together in a directory tree structure as part of a pseudo-filesystem. In NFSv3, all exports are mounted separately.
#Openzfs sharenfs windows#
NFSv4 supports ACLs based on the Microsoft Windows NT model, meaning they provide a richer permissions set and are implemented on more clients than POSIX ACLs. NFSv4 clients are aware of the server’s state and vice versa, which allows for a more graceful recovery after a lost connection. In particular, the locking operations of leasing, timeouts, and client-server negotiation are built into the NFSv4 protocol. By contrast, NFSv4 uses a single RPC service with integrated binding, mounting, and locking, and thus no need for port mapping.

Once a client has mounted an exported NFS share, it can be used like any other directory on the client system. Most client operating systems either ship with an NFS client or have NFS clients readily available for download. Network File System (NFS) is a commonly used protocol for accessing NAS systems, especially with Linux or FreeBSD clients. We’ll also point out configuration parameters which are unique to FreeBSD or OpenZFS, as well as any resources for more information. We’ll provide an overview of each type of share to help guide you in deciding which is most suited to the clients that will be accessing the NAS.
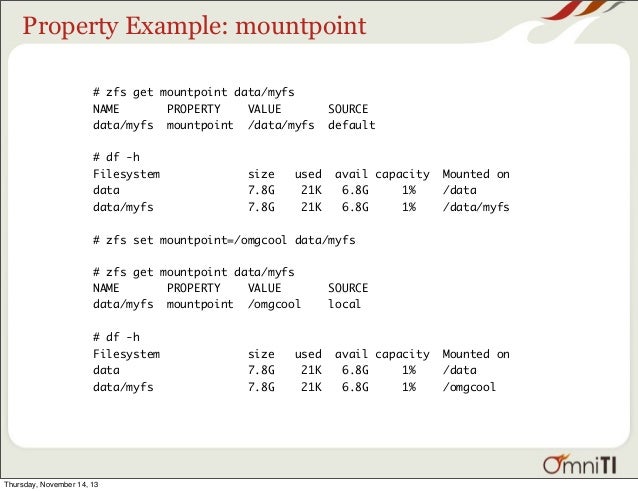
Today, we’ll concentrate on exposing the data on your NAS to the network using NFS, Samba, and iSCSI shares.
#Openzfs sharenfs series#
Previously in this series on building your own vanilla FreeBSD-based NAS solution, we took a look at Building Your Own FreeBSD-based NAS with ZFS and Tuning Your FreeBSD Configuration for Your NAS.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
